
Overview
Modern business are fueled by data; however, it doesn't always come in a useful or usable format. Data Monkey is a data transformation tool designed to make data manipulation simple and automatable ― all through an easy-to-use web application.
Whether you're a data scientist who needs to clean and validate a client's dataset, a developer who needs to build interfaces for client files and external APIs, or a business user that wants to transform a report into a new format ― Data Monkey makes it a quick and painless process.
Automate your workflow
Data Monkey's powerful but intuitive file templates allow you to easily manipulate your data into a consumable format. Define it once ― much like a schema ― and use it forever without needing the help of an expert developer. See our guide on creating a file template for a step-by-step walkthrough.
Explore your data
Receive meaningful insights into the health of your data and automatically detect anomalies ― such as missing or duplicate data, statistical outliers, and much more. See the Generating Reports section for guidance on generating a report or the types of data anomalies for more details.
Detect and handle errors
Data Monkey has meticulous data validation out-of-the-box that ensures every file matches your expectations ― no more surprises! You can choose the level of detail you want to enforce, from the number of columns that appear in the report down to the exact values that are considered valid. See our guide for using validators or the types of validators available for more info.
Guides
Creating File Templates
File templates allow you to define exactly how your files should be transformed. From the number of columns you want to see, the validations you want to enforce, and the way you modify the data itself ― everything is specified here. You can then use your file template to process the files you receive on the Data Monkey application, or even on your own servers.
1. Basic Setup
The main objective of the first step is to upload a sample file with data that you'll use as your baseline. In other words, rather than starting from a blank slate, Data Monkey will pull fields from this file so that you can hit the ground running.
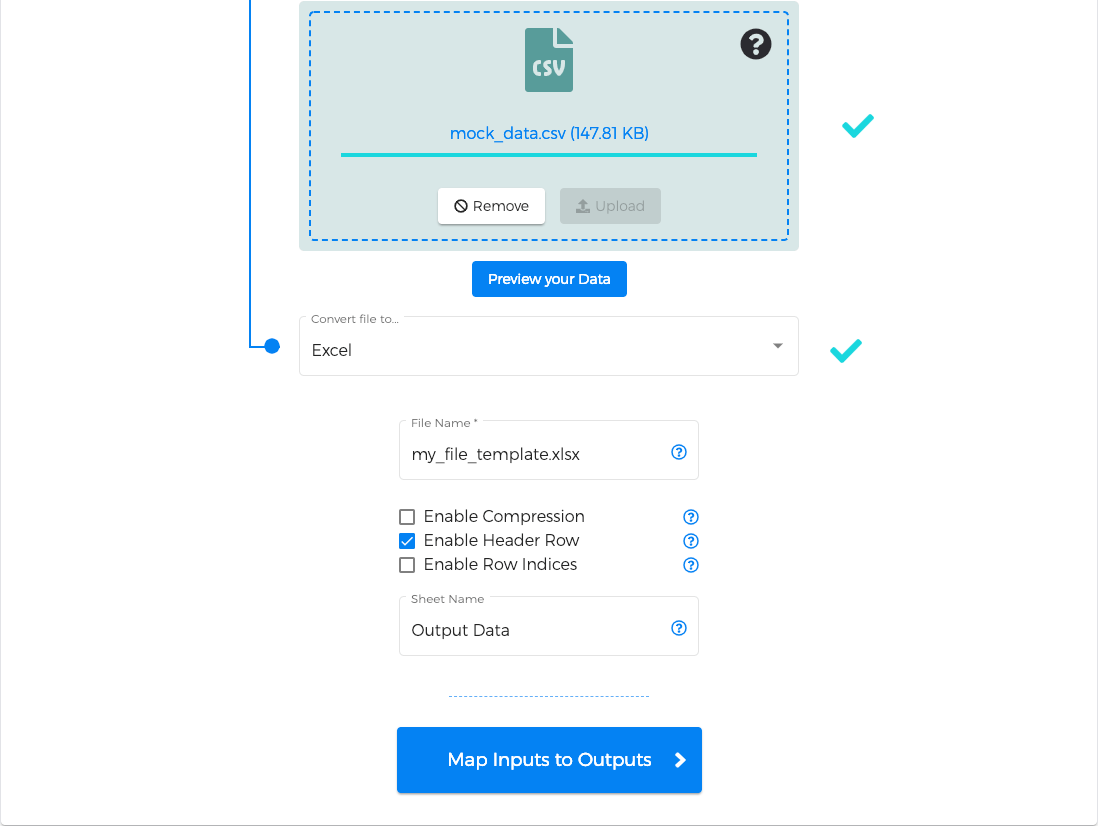
We support several types of files, each with its own set of configuration options; please see the File Options section for more details and downloadable sample files.
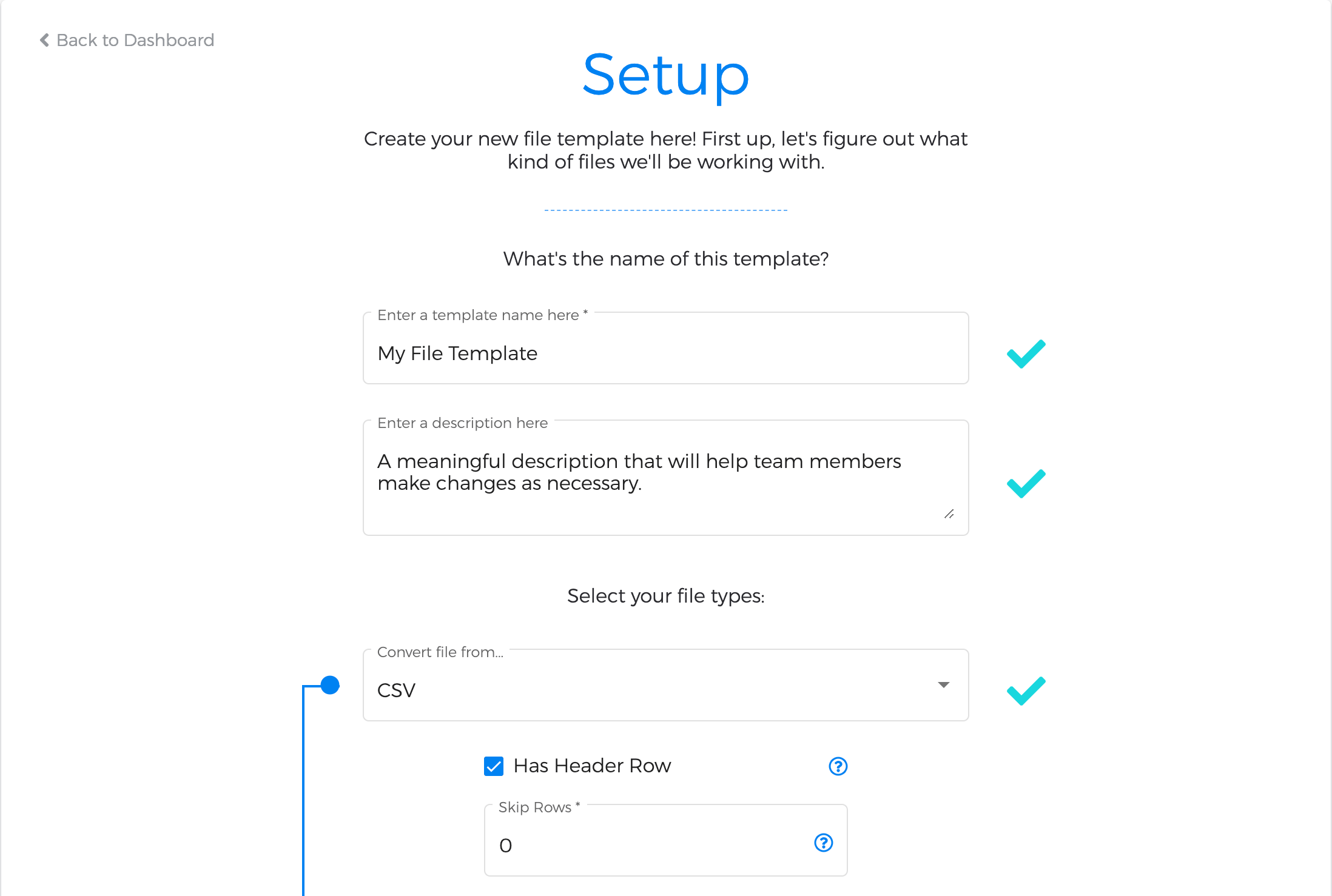
Once you've selected an input file type, you'll need to upload a sample data file to the system. Since this file is only used to set up your initial template, only the first fifty lines of data are extracted. Please refer to our Terms of Service and Privacy Policy when uploading data to our system.
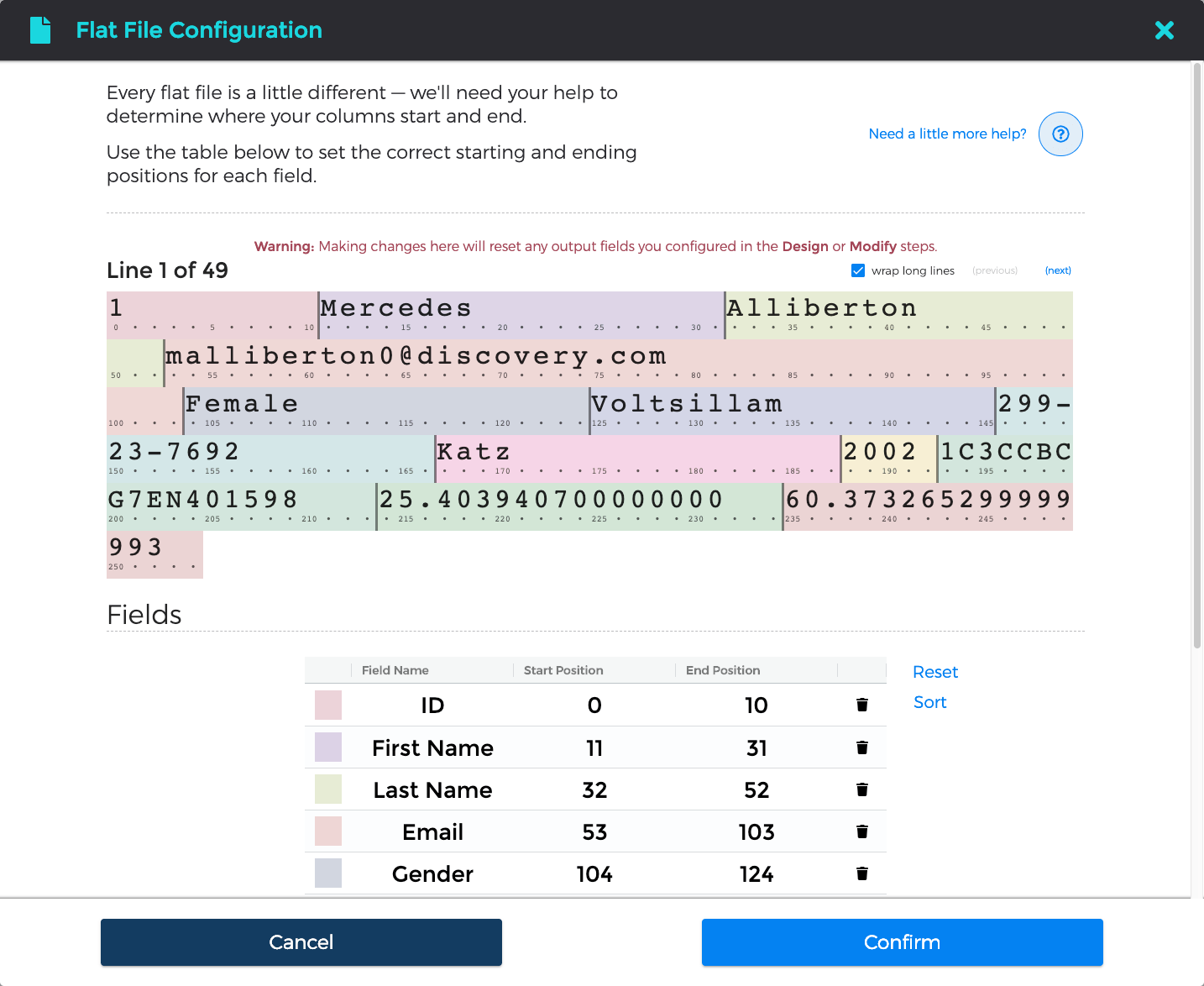
Fixed-width text files ― or flat files ― have an extra, mandatory configuration step. At the top of the Flat File Configuration window, the first
fifty lines of data from your uploaded file are available for viewing; these can be cycled between by clicking the (previous) and (next)
buttons.
These lines of data are pre-divided into several "fields", each clearly marked with a variety of colors. Data Monkey makes an educated guess as to where each field should start and end, but we need to you validate ― or otherwise correct ― these choices in the table at the bottom of the window. Data Monkey will detect when fields overlap with one another, or when data has not been fully included in any field; it is up to you to determine what happens in these situations.
Finally, it may be helpful to rename the fields as necessary if your fixed-width text file did not contain a header row.
2. Design your File Template
Now that Data Monkey has automatically extracted fields from your sample file, we can begin to define what your output file will look like. In other words, our objective in this step is to build the "skeleton" of your output file ― representative of the end result that you would like to generate ― before we start transforming your data itself in the "Modify and Validate Data" step.
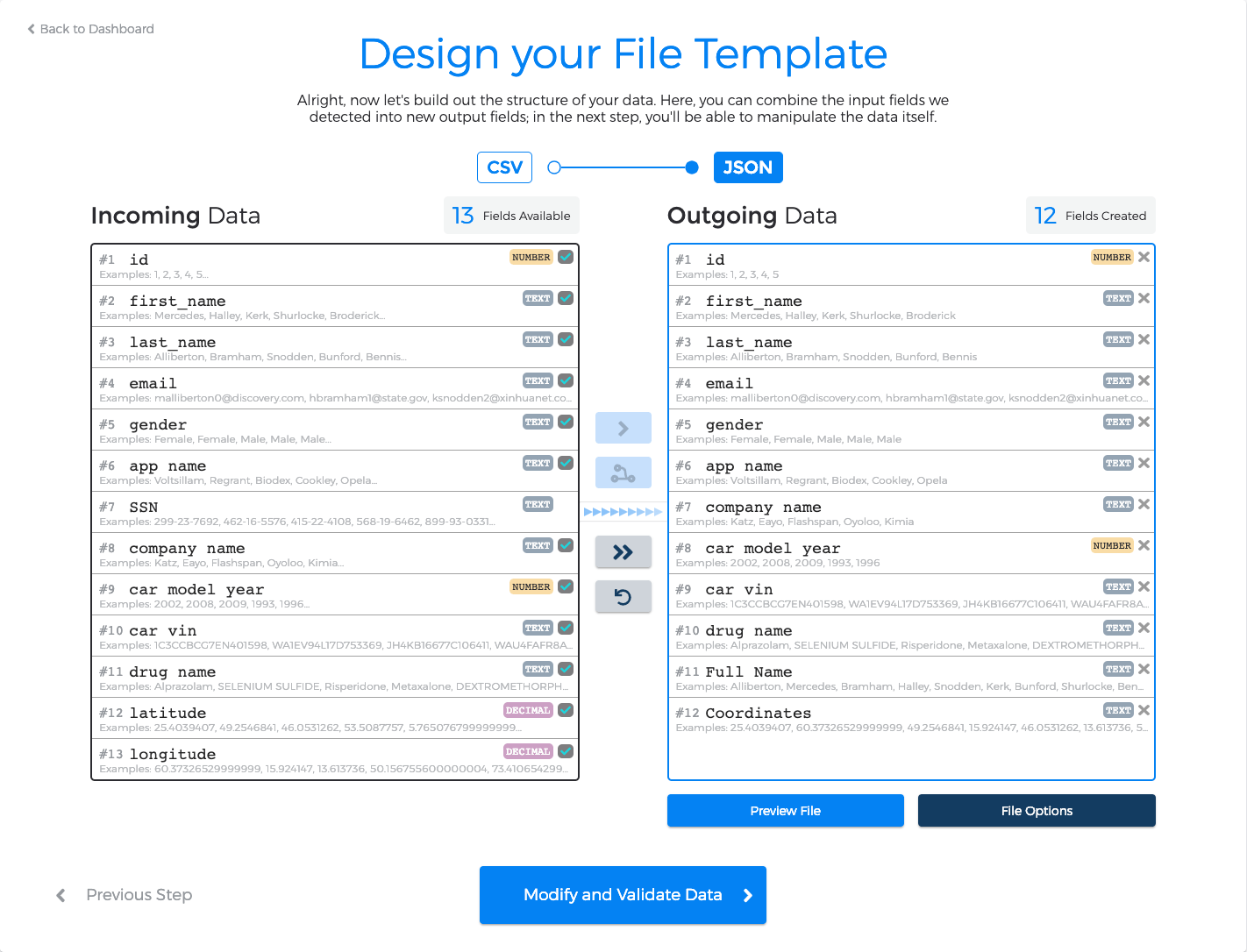
You can transfer any number of your "incoming" data fields directly to your output file, but you can also combine (or "merge") them together. For example, we've decided to combine our "latitude" and "longitude" fields into a single comma-separated "Coordinates" field.
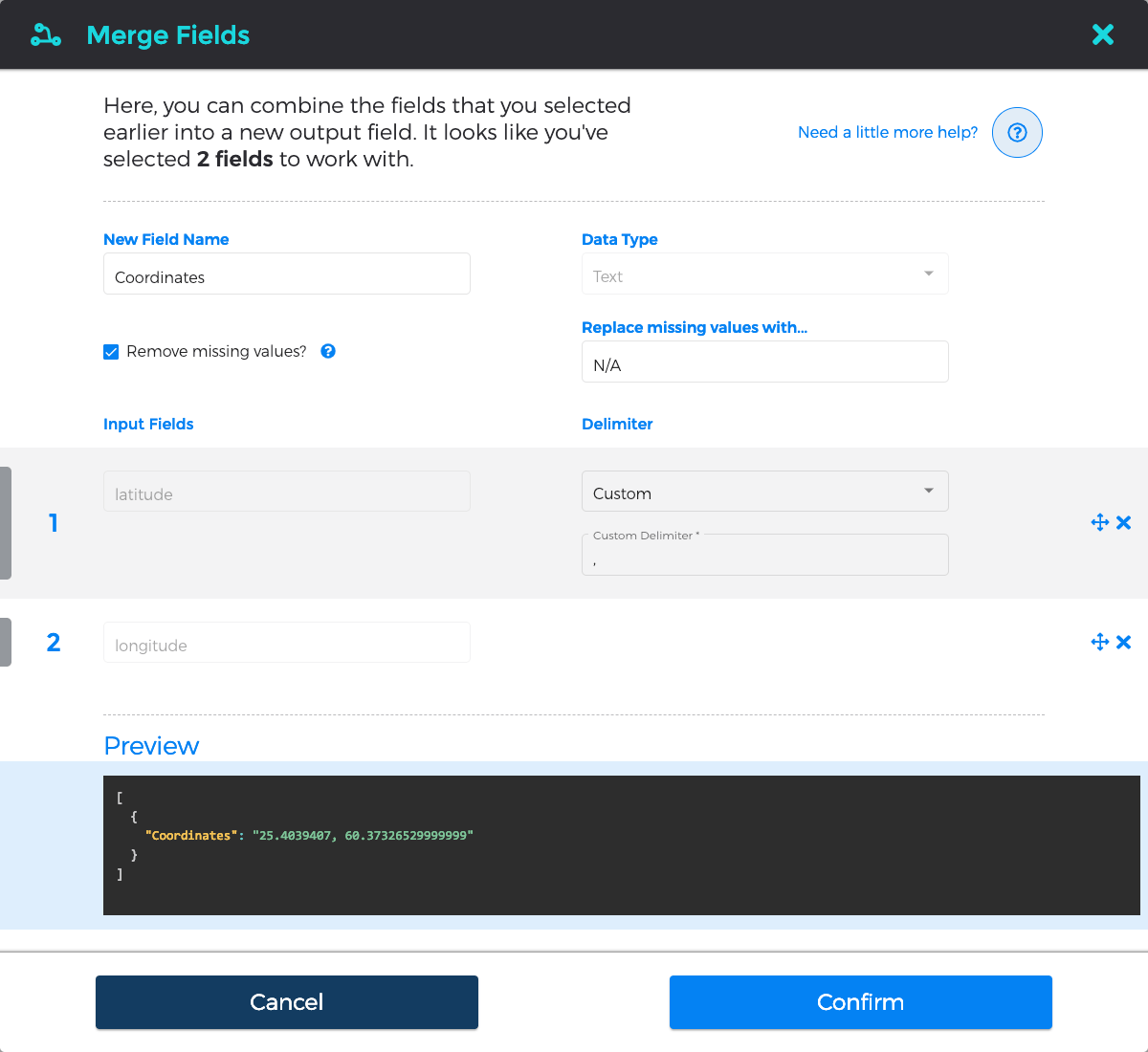
By clicking on an output field, you can rename your output fields as you'd like or change their detected data type, and you can decide how you would like to Data Monkey to deal with missing data (i.e. excluding rows or inserting a default value).
You can also modify options for your output file (see the File Options section) or preview your data at any time.
3. Modify and Validate Data
At this point, we've defined the overall structure of your output file ― we know what fields to expect, as well as their respective data types. We now have the option of manipulating your data itself via powerful filters, modifiers, and validators. These transformations are applied on a field-by-field basis and are processed in the order that you define.
| Transformation Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Filters | Filters let you to remove data that you aren't interested in from your output file. |
| Modifiers | Modifiers allow you to perform complex operations depending on your field's data type. |
| Validators | Validators help make sure that your data conforms to your expectations. |
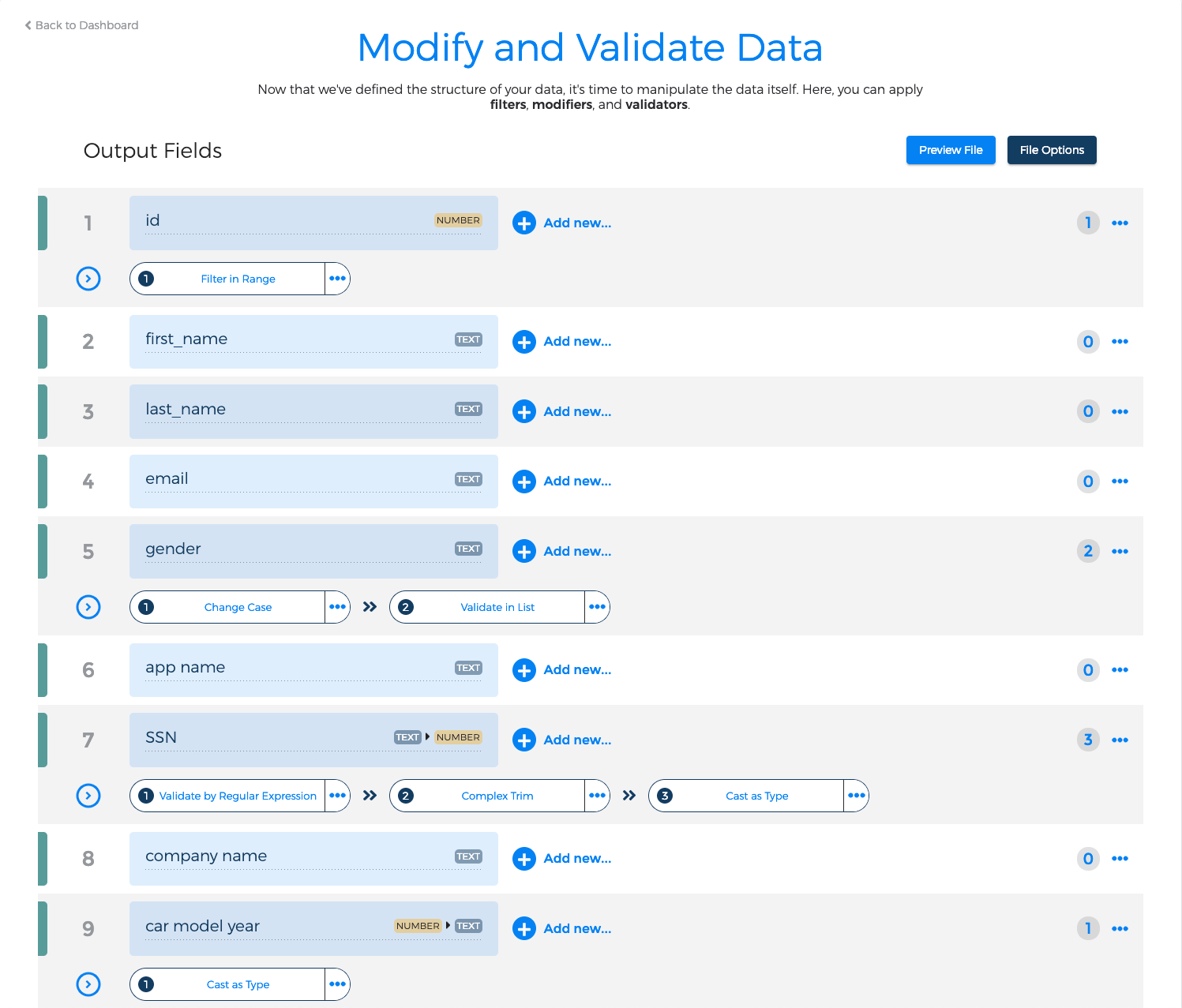
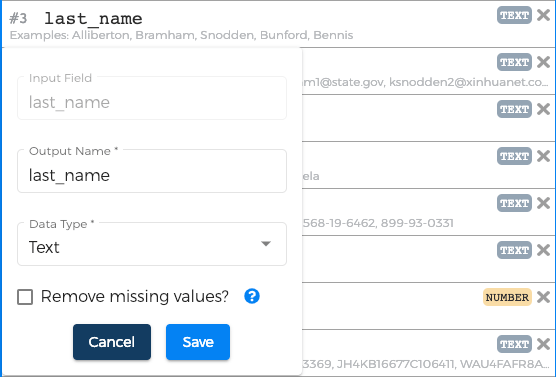
To begin, click on the "Add New" link next to an output fields; this will open a pop-out search window from which you can add transformations to your workflow. The list of available transformations is determined by your field's current data type; however, if you find this too limiting, you have two options: 1) convert ― or cast ― your field to a different data type via the "Cast as Type" transformation; or 2) enable the "Show me all the options, I know what I'm doing" checkbox.
To add a transformation, click on its name in the list of available options.
Once you have added some transformations to your field(s), click the "Done" button to continue. We're not quite done yet: when the search window is closed, a new dialog box will open: most transformations have a small degree of additional configuration that is necessary before they are complete.
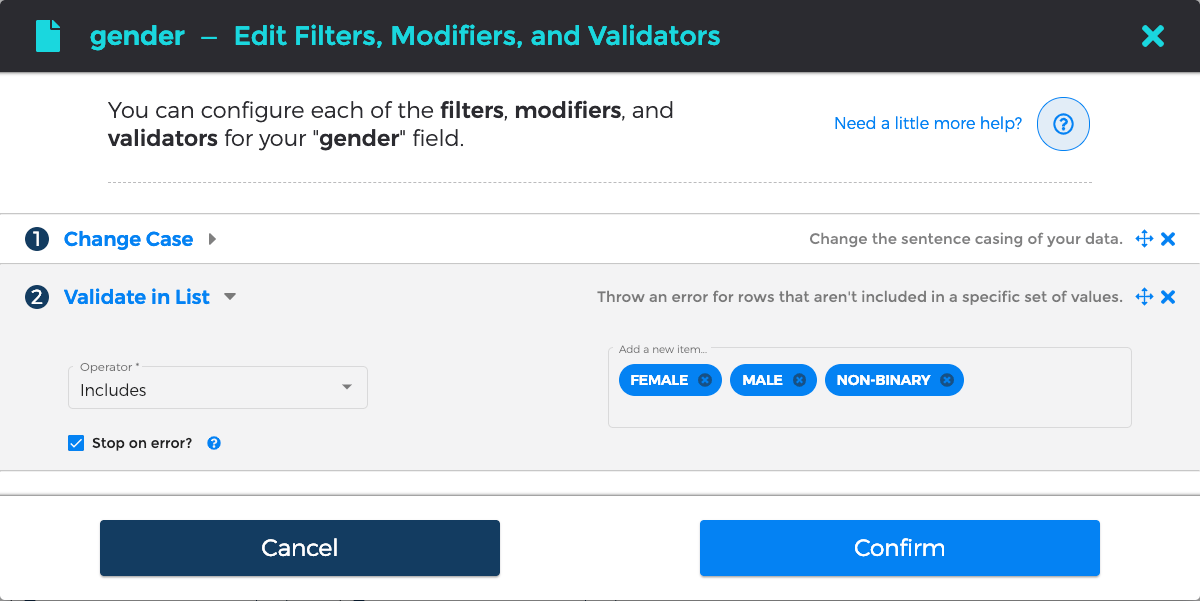
For example, the "Validate by List" transformation needs a list of values to consider valid (or invalid, if you prefer); in the image below, we are validating that the "Gender" column will only contain "MALE", "FEMALE", and "NON-BINARY" values. By enabling the "Stop on error?" checkbox, we have additionally indicated that we would like to treat any data not in this exact list as erroneous and to stop processing files early.
Finally, you can copy transformations from one field to another ― as long as they are of the same data type ― through the pop-out menu on the right.
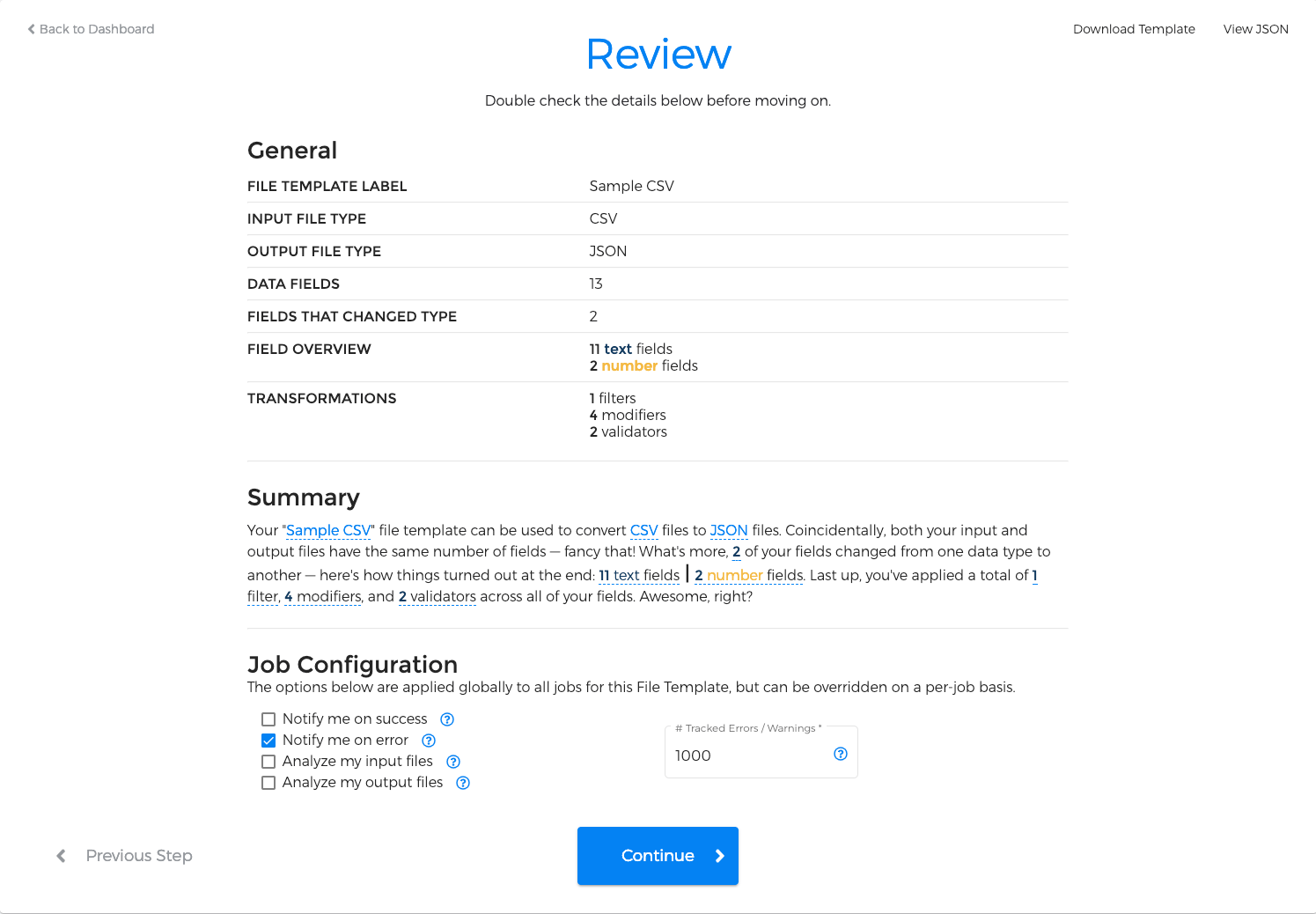
4. Review and Next Steps
We're all done! We've finished setting up your file template, meaning you can now use your template to process any number of files in an identical manner with all of the benefits of Data Monkey's powerful data transformation and analytics suite.
You're also able to set several default values for how you'd like jobs to be processed in the future.
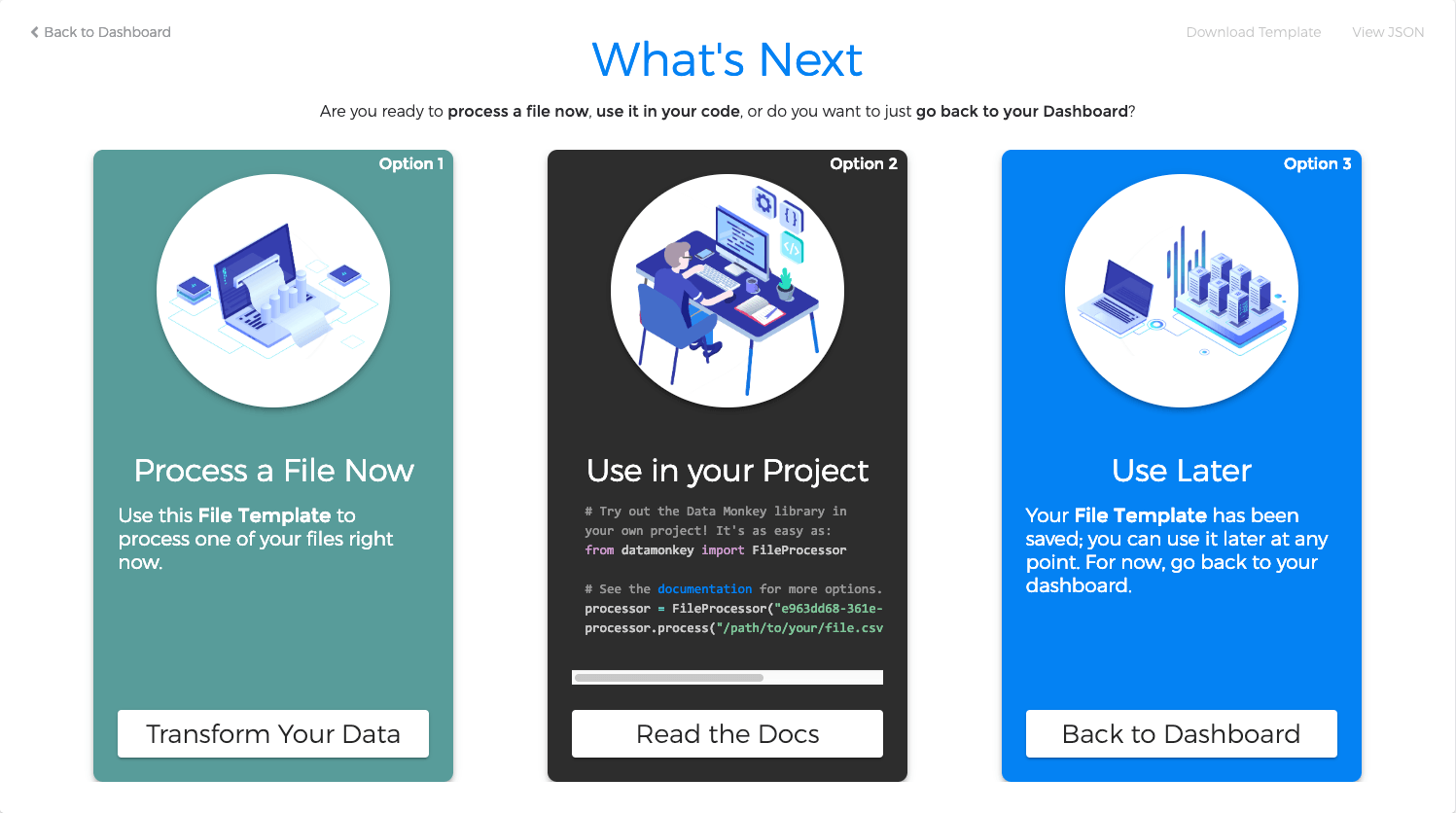
Once you've saved your file template, you have three immediate options: 1) process a file directly; 2) use your new file template in one of your projects; 3) or simply use it at a later date.
Processing Files
You can use Data Monkey to process a file using a file template you've created.
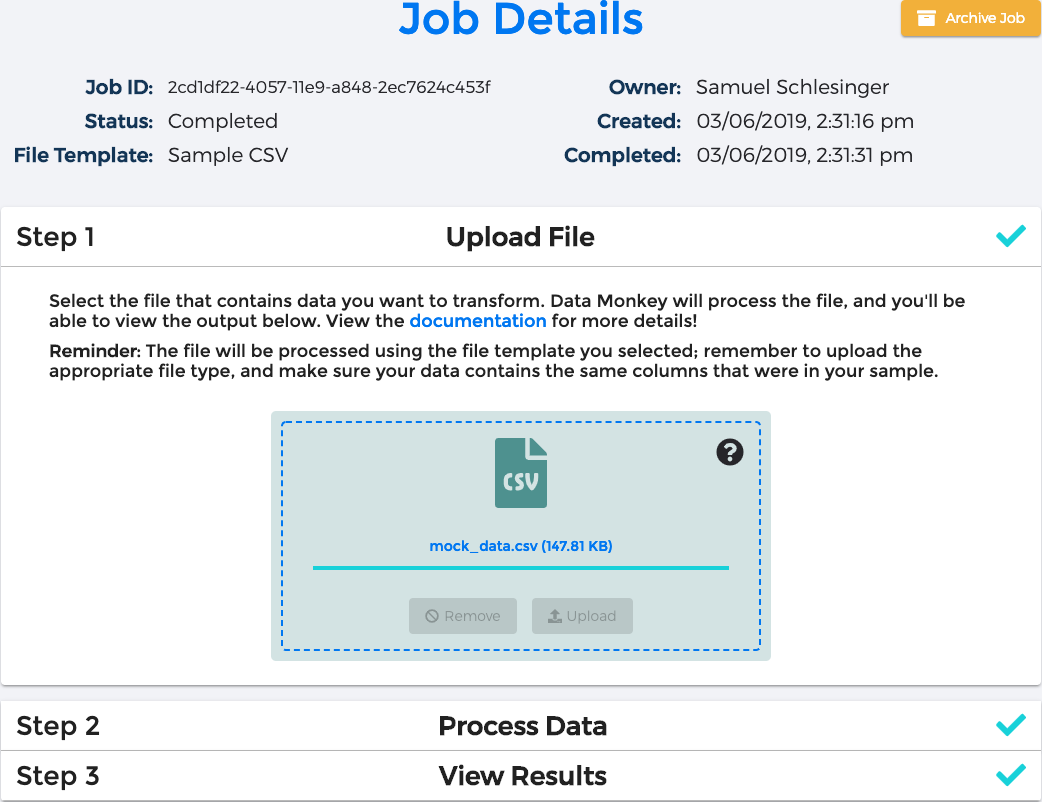
Using Data Monkey
All of your file templates are listed on the Dashboard ― press the "Transform Data" button next to the file template you'd like to use. On the next screen, upload the file you'd to process; once done, our team of capable monkeys will immediately begin working on your data.
As this happens, you'll see status messages to let you know how long we expect your job to take; depending on the size of your file and the overall complexity of your template, it could take anywhere from mere seconds to several minutes to process. If you prefer, you can edit your file template to enable email notifications for when your job has finished processing successfully or with errors.
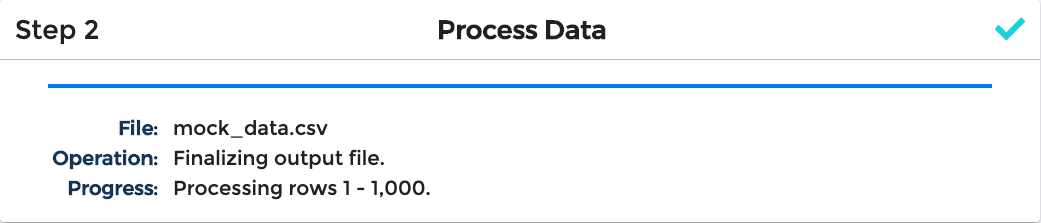
Once file processing is finished, you'll be able to download the output file that was generated, as well as the original input and any errors or warnings that may have occurred. Data Monkey will retain the results for 60 days, after which these files will be deleted. However, you can also choose to explicitly delete your files at any time by clicking the "Archive" button.

Using Your Servers
Data Monkey offers a free Python package that enables you to process files on your own servers; all it takes is a few lines of code and the ID of your file template. Check out our guide on Github for details!
Generating Reports
Data Monkey is proud to offer a powerful analytics and reporting suite that provides meaningful insights into your data. We distill each field down to a few defining factors, such as its inferred data type (such as a phone number or date), whether it has unique, duplicate, or missing values, and broad range of potential anomalies or oddities (see more details).
To generate a report, navigate to the "Analyze Files" section of the Dashboard, and click the "Analyze File" button. You'll be able to upload your file and configure a number of options depending on its type; see the File Options section for more details.
Click the "Generate Report" button to send our highly-trained crew of monkeys to work. It usually takes between a few seconds and few minutes, depending on the size and complexity of your data, for your report to be generated. You'll receive status messages as the report generates, and can optionally choose to be notified by email once the reporting process is complete.
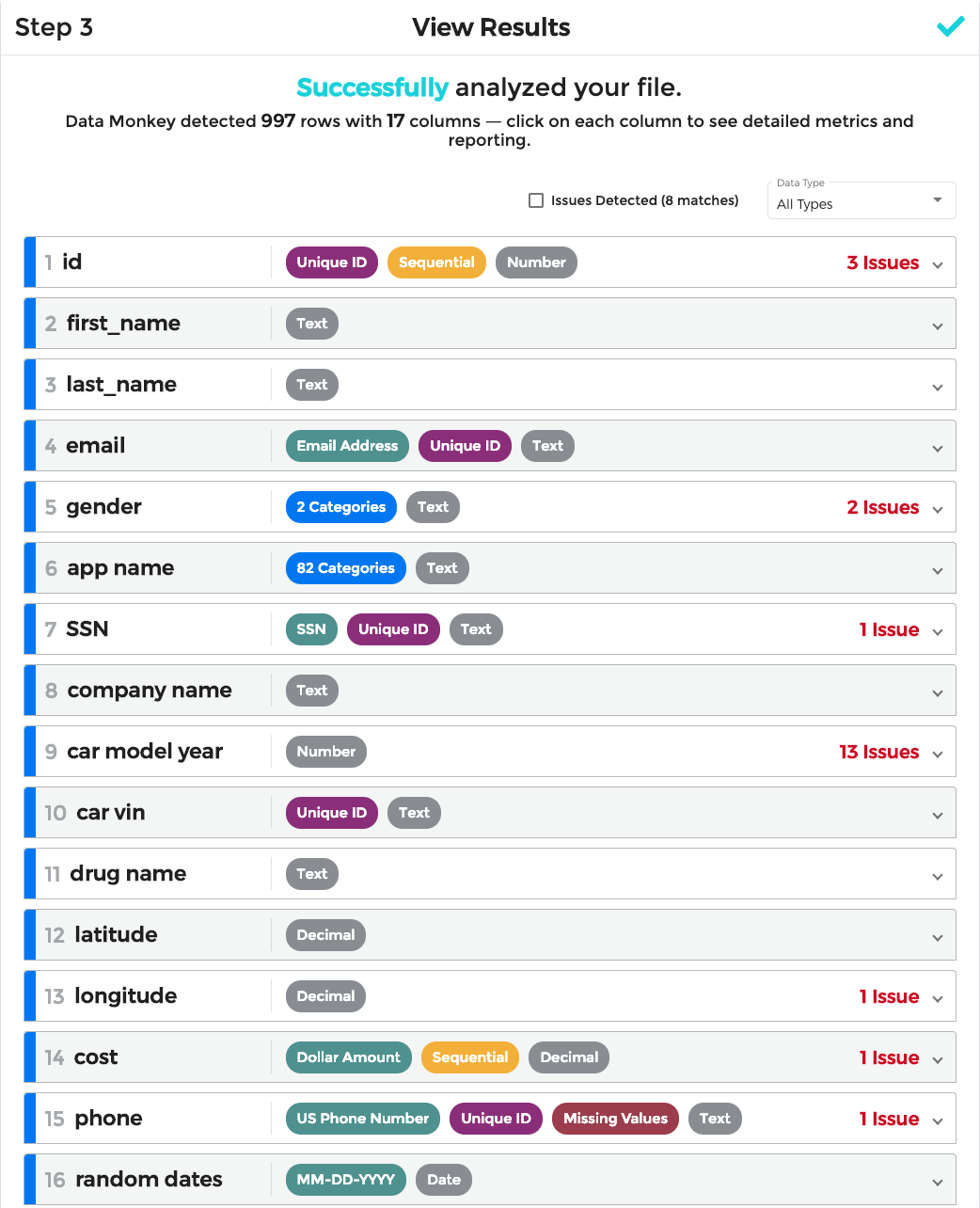
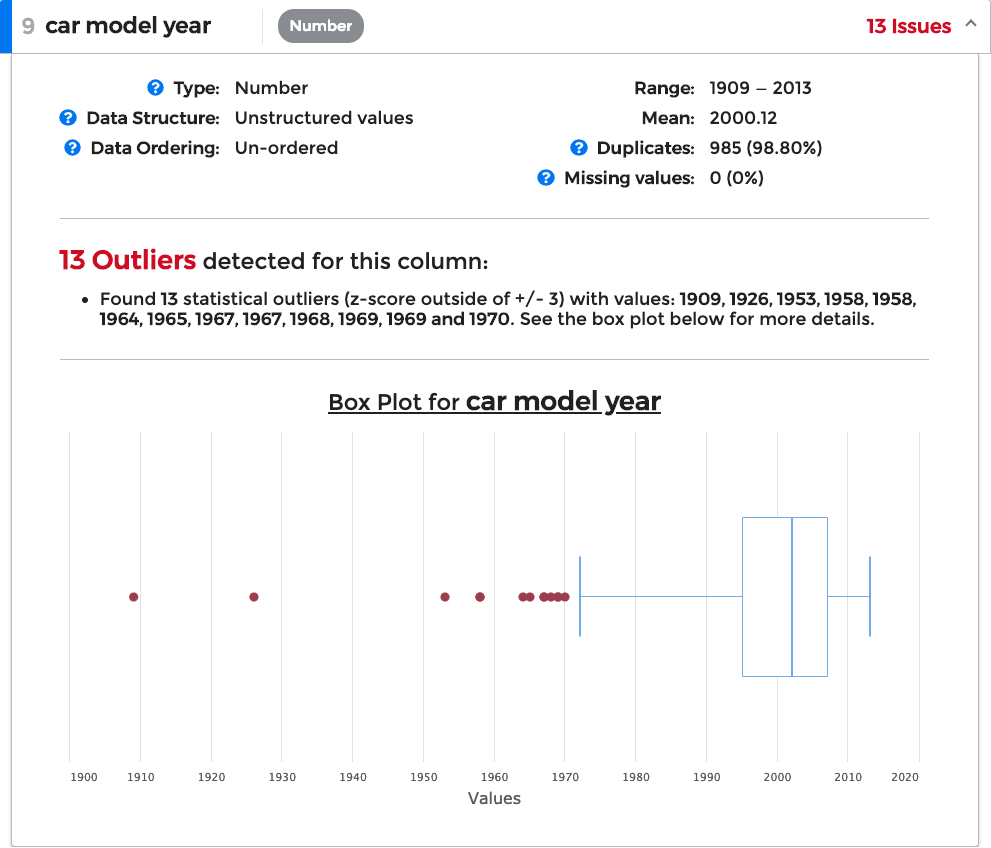
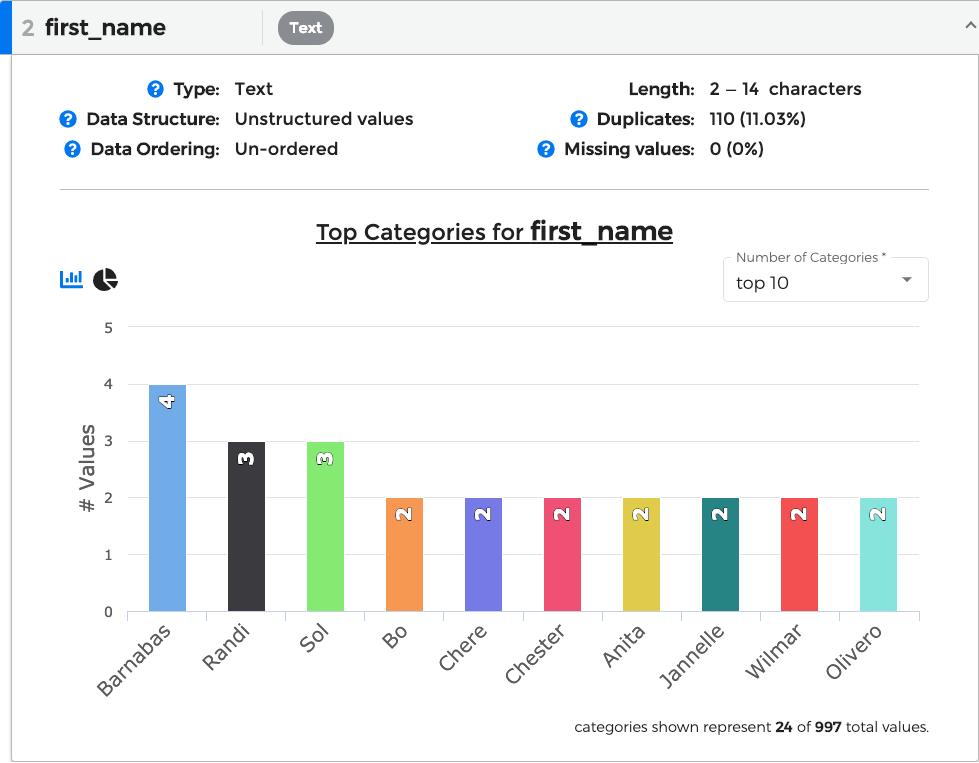
You can expand each of these sections to receive a more detailed view of the column, including a list of issues detected and any related graphs.
We're constantly improving our reporting capabilities and would love to hear your ideas on what you'd like to see, or feedback on what you found (or didn't find!) helpful ― reach out to us at feedback@data-monkey.com!
Additional Help
If you couldn't find what you needed in the guides, we're always available to help! Please feel free to reach out at help@data-monkey.com and we'll be in touch.
Appendix
File Options
Excel Files (sample file)
Note: Please make sure your Excel files do not have any special formatting (such as merged fields).
| Option | Applies To | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Skip Rows | Input Only | The number of rows to skip before loading data. |
| File Name | Output Only | The name of the output file that will be generated. |
| Enable Row Indices | Output Only | If checked, the first column will be the index of the current row. |
| Enable Compression | Output Only | If checked, the output file will be compressed in a ZIP archive. |
| Sheet Name | Input & Output | The name of the sheet that will contain the output data. |
| Enable Header Row | Input & Output | If checked, the first first row in the file should contain the column names. |
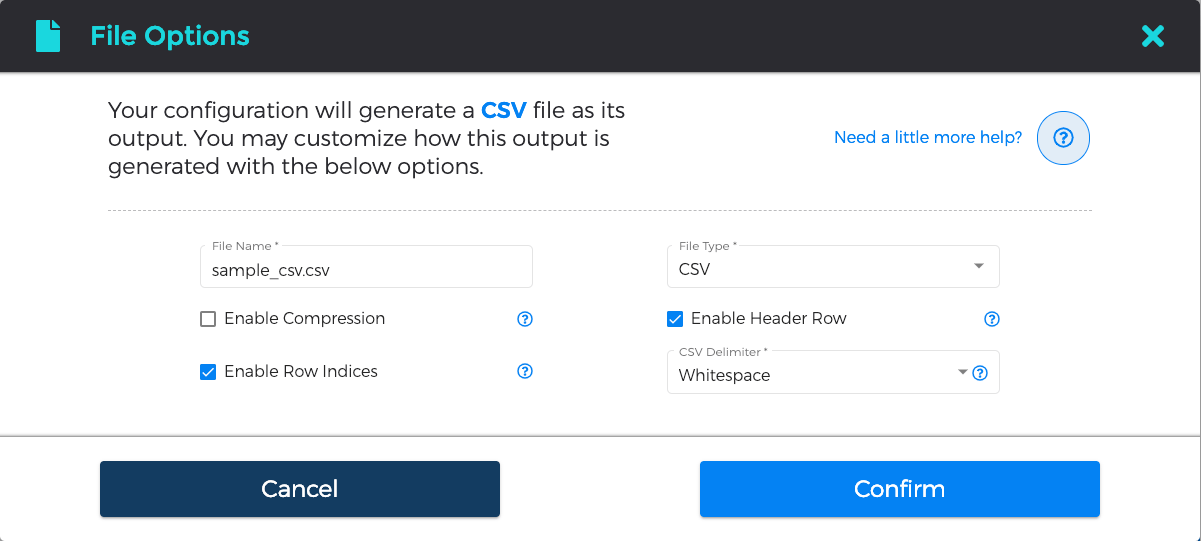
CSV Files (sample file)
| Option | Applies To | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Skip Rows | Input Only | The number of rows to skip before loading data. |
| File Name | Output Only | The name of the output file that will be generated. |
| CSV Delimiter | Output Only | The character(s) that will be used to delimit fields in the CSV file (default value is a comma). |
| Enable Row Indices | Output Only | If checked, the first column will be the index of the current row. |
| Enable Compression | Output Only | If checked, the output file will be compressed in a ZIP archive. |
| Enable Header Row | Input & Output | If checked, the first first row in the file should contain the column names. |
JSON Files (sample file)
Note: Please make sure your JSON files do not have nested data.
| Option | Applies To | Description |
|---|---|---|
| File Name | Output Only | The name of the file that will be generated. |
| Indent | Output Only | The number of spaces used to indent each line object; choose 0 for a very compressed file, or 2 for a 'prettier', formatted file. |
| Enable Compression | Output Only | If checked, the output file will be compressed in a ZIP archive. |
Fixed-width Text Files (sample file)
| Option | Applies To | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Skip Rows | Input Only | The number of rows to skip before loading data. |
| File Name | Output Only | The name of the output file that will be generated. |
| Enable Compression | Output Only | If checked, the output file will be compressed in a ZIP archive. |
| Enable Header Row | Input & Output | If checked, the first first row in the file should contain the column names. |
Filters
Filters can be used to automatically remove entries you want to ignore.
Filter in Range
Filter out any values that do not fit within the defined range.
Usable by: numbers, decimals, dates.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Minimum | The lower end of the range of acceptable values, inclusive (i.e. 1 - 10). |
| Maximum | The upper end of the range of acceptable values, inclusive (i.e. 1 - 10). |
Filter by Value
Filter out any values that do not match the defined equality.
Usable by: numbers, decimals, dates.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | An equality operator (LT, LE, GT, GE, EQ, NE). |
| Value to filter by | The number or date to filter by. |
Filter by List
Filter any values that are not included in a defined list. Can also be inverted to filter out values that are in the list instead.
Usable by: text, numbers, decimals, booleans.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | A list operator: includes or excludes. |
| Values | A list of values to be used as a whitelist or blacklist. |
Filter with Regular Expression
Filter any values that are not do not match against the user-defined regular expression.
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Expression | A regular expression. |
Filter by Length
Filter for text values with lengths that do not match the defined equality (e.g. <= 4 characters)
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | An equality operator (LT, LE, GT, GE, EQ, NE). |
| Length | The length of text in characters. |
Filter if Text Appears
Filter any values that do not include a user defined text fragment. Can be inverted to filter entries that include the fragment instead.
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | An list operator: includes or excludes. |
| Text fragment to filter by | The text to search for. |
Modifiers
Modifiers are used to change the data itself, similar the calculation methods available in Excel.
Mathematical Operation
Perform a standard mathematical operation on the data (e.g. add, subtract, multiply, divide).
Usable by: number, decimal.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | An mathematical operator (ADD, SUBTRACT, MULTIPLY, DIVIDE). |
| Value | The number value to perform math operations with. |
Complex Trim
Remove a defined number of characters from the right or left side of the text value.
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | A direction to trim / remove characters from: from left or from right. |
| Value | The number of characters to remove from values. |
Remove Whitespace
Remove any blank or whitespace characters from the text value.
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | A direction to remove whitespace from: from left, from right, or from both. |
Change Case
Chase the case of the text value.
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | The casing to convert to: uppercase, lowercase, or capitalize. |
Remove Text
Remove a user-defined text fragment from the text value (if found).
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Value | The word or phrase to remove from all values. |
Append Text
Append a text fragment to the left or right side of the text value.
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | A direction to append characters to: to left or to right. |
| Value | The word or phrase to append to all values. |
Replace Text
Similar to Remove Text, this modifier will search for a user-defined text fragment -- but will replace
the value with another user-defined text fragment.
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Old Value | The old word or phrase that should be replaced. |
| New Value | The new word or phrase will be used in place of the old value. |
Change Date Format
Change the format of a date value (e.g. 01-01-2018 => Jan 01, 2018)
Usable by: date.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | The date format to convert to. |
Round Number (Precision)
Round a decimal value to a user-defined precision.
Usable by: decimal.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Number of Decimal Points | The number of decimal points values should be rounded to have. |
Cast as Type
Casting the value to another type will allow you to use modifiers for that type. For example, you could cast number values
to text values, which would allow you to Append Text (e.g. 5 => 5 apples).
Usable by: text, numbers, decimals, booleans.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Value | The data type that values should be converted to. May not always work, i.e. the word "hello" is not a valid number. |
Validators
Validators are used to define exactly which values you expect to see. We know that some issues are more important than others; you can choose to stop processing if invalid data appears, or simply log it as a warning.
Validate in Range
Validate that all values fit within the defined range.
Usable by: numbers, decimals, dates.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Minimum | The lower end of the range of acceptable values, inclusive (i.e. 1 - 10). |
| Maximum | The upper end of the range of acceptable values, inclusive (i.e. 1 - 10). |
Validate Value
Validate that all values match the defined equality expression.
Usable by: numbers, decimals, dates.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | An equality operator (LT, LE, GT, GE, EQ, NE). |
| Value to validate | The number or date to validate. |
Validate in List
Validate that all values match against the values in the defined list. Can be inverted to check that no values match against the values in the defined list instead.
Usable by: text, numbers, decimals, booleans.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | A list operator: includes or excludes. |
| Values | A list of values to be used as a whitelist or blacklist. |
Validate with Regular Expression
Validate that all values match against the defined regular expression.
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Expression | A regular expression. |
Validate Length
Validate that all text values have a character length that matches the defined equality (e.g. >= 4 characters)
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | An equality operator (LT, LE, GT, GE, EQ, NE). |
| Length | The length of text in characters. |
Validate Text Contains
Validate that all text values contain the defined text fragment. Can be inverted to validate that all
text values do not contain the text fragment instead.
Usable by: text.
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| Operator | An list operator: includes or excludes. |
| Text fragment to validate | The text to search for. |
Data Anomaly Detection
Data Monkey's reporting checks for many common issues for each column or field the data you upload. See the list below for an explanation of each type of issue that can occur:
Missing Values in Sequence
The data field is sequential if it seems to follow a consistent pattern; for example, you might have a number field that increases by 1 for each row (like an ID or index), or maybe a date field with one entry for each day of the year. If Data Monkey detects a sequence, it looks for gaps where data may be missing. This detection currently works for number, decimal, and date fields. For example, you have a 'Transaction Date' column with a date range for each day between Jan 1, 2018 through Dec 31, 2018 ― but Feb 12, 2018 seems to be missing.
Blank or Missing Values
If the data field is mostly populated (>99% of rows have a value), Data Monkey will check for entries with missing or null values. For example, you have an 'Email Address' column with 10,000 rows, but 3 rows have missing data ― you'll see those 3 rows included in the issues report.
Duplicate Values
If the data field seems to contain all unique entries, Data Monkey will include any duplicates in the issues report. For example, you have an 'ID' column with values ranging from 1 through 1000, but the ID 200 is seen twice.
Values with No Category
If the data field seems to be categorical, meaning all values fit within a set of categories, any values that are unique will be included in the issues report. For example, you have a 'Status' column with two categories ('COMPLETE', 'INCOMPLETE') that are repeated many times ― but the value 'TEST' only appears once.
Invalid Values
Data Monkey attempts to match each data field with an field type, e.g. Phone Number, SSN, Email Address, etc. If the majority of entries do match a field type, the values that don't conform will be included in the issues report. For example, Data Monkey detects that a field contains email addresses, but the value 'Hello!' does not match.
Miscellaneous
Data Types
| Data Type | Description |
|---|---|
number |
An integer / whole number with no decimal places (i.e. 5 or 10). |
decimal |
A floating point number with decimal places (i.e. 3.14 or 0.5. |
text |
A plain text word or phrase. |
date |
A date in any of our supported date formats. |
boolean |
An "truthy" (true, 1, etc.) or "falsy" (false, 0, etc.) value. |
Date Formats
| Date Format | Example |
|---|---|
DD-MM-YYYY |
30-01-2019 |
DD-MMM-YYYY |
30-Jan-2019 |
MM/DD/YYYY |
01/30/2019 |
MM-DD-YYYY |
01-30-2019 |
MMM-DD-YYYY |
Jan-30-2019 |
YYYY-MM-DD |
2019-01-30 |
Equality Operators
- Less Than (
LT) - Less Than or Equals (
LE) - Greater Than (
GT) - Greater Than or Equals (
GE) - Equals (
EQ) - Not Equals (
NE)
Mathematical Operators
- Addition (
ADD) - Subtraction (
SUBTRACT) - Multiplication (
MULTIPLY) - Division (
DIVIDE)